|
TopNax |
|
Home†††††† Previous††††††† AMD page†††††††† Intel page†††††††† Next |
|
Brazos Performance Preview:†† AMD E350 Benchmarked |
|
Last week I mentioned that I had recently spent some time with AMD down in Austin, TX, benchmarking its upcoming Brazos platform. The Brazos platform is composed of an AMD Zacate or Ontario APU and the Fusion Controller Hub (a South Bridge based on the SB800 series). Brazos systems will run the gamut of mainstream notebook, netbook and nettop segments ranging from $299 to around $500. While AMD let us reveal the fact that we tested Brazos, we weren't allowed to publish numbers last week. Today, we can. I didnít have much time with Brazos. The AMD briefing started at 9AM, but AMD wanted to go through some marketing slides and answer questions before letting us at Brazos. Going into this whole thing I was worried that I wouldnít have enough time to run everything I wanted to run. You see, the system I had access to wasnít pre-configured. It had Windows 7 x64 loaded on it, drivers installed and PCMark Vantage - but everything else was up to me. Despite having a 128GB Crucial RealSSD C300, installing a dozen applications and games still took hours on the system. I asked AMD if I could at least begin copying/installing some applications before we started the briefing, they gladly entertained my request. I brought an SSD full of applications, games and benchmarks that I wanted to run on the Brazos platform. I purposefully avoided any large test suites (PCMark Vantage, SYSMark) because they would eat up a lot of time and I had no idea how long the rest of the benchmarking would take.
I also didnít run any of our media streaming suite. The Zacate/Ontario APUs feature AMDís UVD3 engine and should, in theory, have similar media playback features to the Radeon HD 6000 series. Of course once we have final systems itíll be easier to put this to the test. I was mainly interested in characterizing the CPU and GPU performance of Brazos, the two major unknowns. I didnít get into the full swing of testing until just before 11AM, and we had a hard stop at 5PM. That didnít leave a ton of time, but I believe it left enough to get a good idea for what Brazos will perform like in the real world. As I mentioned in Part 1 of our coverage, the system felt snappy. I had the 11-inch MacBook Air on hand (it served as my Excel-runner while I benchmarked) and interacting with the OS felt no different between the Brazos system and the 1.6GHz MBA. That being said, the MBA is technically much quicker (and more expensive). |
|
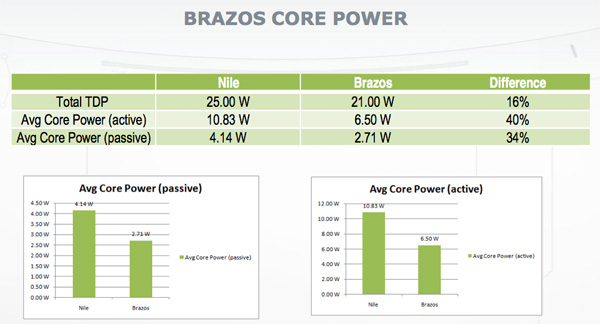
The system I tested had AMDís E-350 processor, the highest end APU youíll find on a Brazos. This is the chip youíll find in $400 nettops and notebooks in the $400 - $500 range. This puts its direct competition as really expensive Atom based netbooks, Pentium dual-core notebooks and low end Core i3 notebooks. While the latter two should easily outperform the E-350 in CPU intensive tasks, the GPU comparison is another story entirely. Itís also worth noting that the E-350 carries an 18W TDP (including graphics). During my testing I measured a maximum total system power consumption of around 30W (including the 1366 x 768 LCD panel) while playing games and around 25W while encoding H.264 on the two Bobcat cores. The system idled around 15W however AMD cautioned me that this number was unnaturally high. Final Brazos systems will be far more power optimized and AMD expects numbers to drop down to as low as 5.6W. AMD is confident we will see Brazos based systems deliver well beyond 6 hours of battery life. AMD's goal is to deliver Atom like battery life and form factors, with a real GPU and hopefully better than Atom performance. We spent our time in Austin trying to find out if its goals were realistic. |
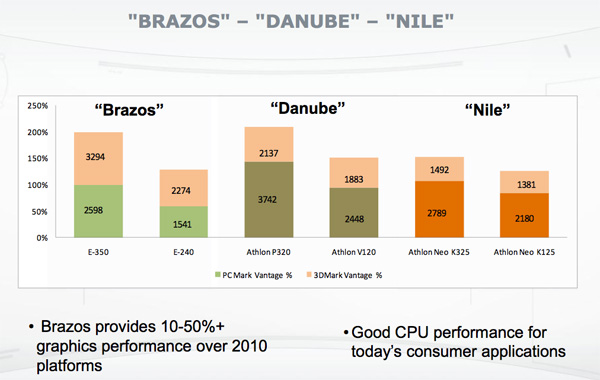
Setting Performance ExpectationsAMD provided this slide of PCMark Vantage and 3DMark Vantage performance of Brazos compared to its existing mobile platforms (Danube and Nile): If you look at the PCMark Vantage numbers you'll see that AMD's E-350 provides roughly the same performance as an Athlon V120. That's a single core, 45nm chip running at 2.2GHz with a 512KB L2 cache. Or compared to a dual core processor, it's within striking distance of the Athlon Neo K325 which features two cores running at 1.3GHz and 1MB L2 per core. The GPU performance however tells a very important story. While AMD's previous platforms offered a great deal of CPU performance and an arguably imbalanced amount of GPU performance, Brazos almost does the opposite. You get a slower CPU than most existing mainstream platforms, but a much better GPU. In the sub-$500 market, you're not going to get much in the way of a discrete GPU. What AMD is hoping for is that you'll be happy enough with Brazos' CPU performance and be sold on its GPU performance and total power consumption. From AMD's standpoint, there's not much expense involved in producing a Zacate/Ontario APU, making Brazos a nice way of capitalizing on mainstream platforms. The 75mm2 die itself is smaller than most discrete GPUs as well as anything Intel is selling into these market segments.
The ComparisonBrazos, like Atom, will fight a two front war. On the one hand you have the price comparison. The E-350 will be found in notebooks in the $400 - $500 range according to AMD. That puts it up against mainstream notebooks with 2.2GHz Intel Pentium DC and 2.26GHz Core i3-350M processors. Against these platforms, Brazos won't stand a chance as far as CPU performance goes but it should do very well in GPU bound games. I've included results from a 2.2GHz Pentium dual-core part (1MB L2 cache) as well as a simulated Core i3-350M in the mobile IGP comparison. The other front is, of course, the ultraportable space. Here you'll see the E-350 go head to head with dual-core Atom, Core 2 ULV and Arrandale ULV parts. AMD's CPU performance should be much more competitive here. From this camp we've got the Atom D510 (close enough to the N550) and a simulated Core i3-330UM. The expectations here are better CPU performance than Atom, but lower than Arrandale ULV. GPU performance should easily trump both. |
Memory and Cache LatenciesThe Brazos platform was configured with 4GB of DDR3-1066 memory. The IDF system had memory running at DDR3-1333, however AMD had to decrease clocks presumably to meet validation requirements for final silicon. I measured an 86.9ns trip to main memory, a 3 cycle L1 and a ~22 cycle L2 cache. That's a lower latency memory interface than Atom or Core 2 based processors, but a higher latency L2. CPU Performance: Better than Atom, 90% of K8 but Slower than Pentium DC
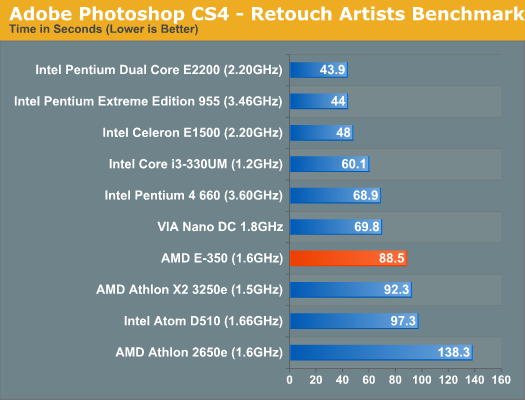
AMD's performance target for Bobcat was 90% of the performance of K8 at the same clock speed and our Photoshop CS4 benchmark shows that AMD can definitely say that it has met that goal. At 1.6GHz the E-350 manages to outperform a pair of K8s running at 1.5GHz in the Athlon X2 3250e. Unfortunately for AMD, Intel's Pentium dual-core running at 2.2GHz is much quicker. Most notebooks in the $400+ range have at least a 2.2GHz Pentium. Even the Atom D510 isn't far behind. AMD tells me that in general purpose integer tasks, the E-350 should do well and it may even exceed AMD's 90% design target. However in higher IPC workloads, for example many floating point workloads, the E-350 is constrained by its dual issue front end. In these situations, the out of order engine is starved for instructions and much of Bobcat's advantage goes away.
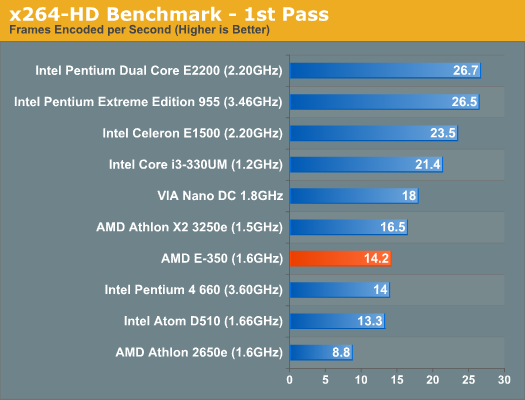
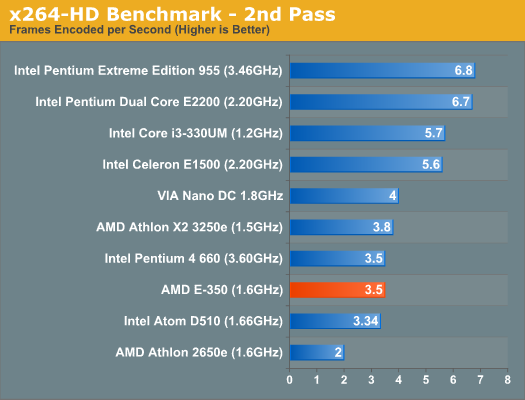
Our x264 HD test has the E-350 performing within 86 - 92% of the Athlon X2 3250e, once again meeting AMD's design targets. Unfortunately, this isn't much faster than an Atom - mostly thanks to Atom's Hyper Threading support. Although not an out of order architecture, Atom gets a healthy efficiency boost by being able to execute instructions from two threads per core. Once again, compared to a 2.2GHz Pentium, the E-350 isn't close. Even VIA's dual core Nano is faster. When it comes to power consumption however, the E-350 can't be touched. I measured max system power consumption at 25.2W while running the x264 encode test. With the exception of the Atom D510, the rest of the desktop platforms here consume much more than that at idle (much less under load).
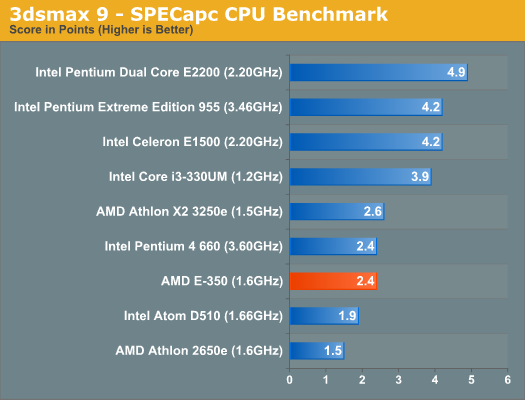
Despite being a offline 3D rendering benchmark, our 3dsmax 9 test does fall in line with expectations. The E-350 delivers 92% of the performance of the Athlon X2 3250e and outperforms the Atom D510 by 26%. Unfortunately for AMD, the Pentium dual-core holds onto a significant performance advantage here. Clock for clock, Bobcat won't be able to do much against anything Core 2 based. The real advantage here will be GPU performance. Single Threaded Performance
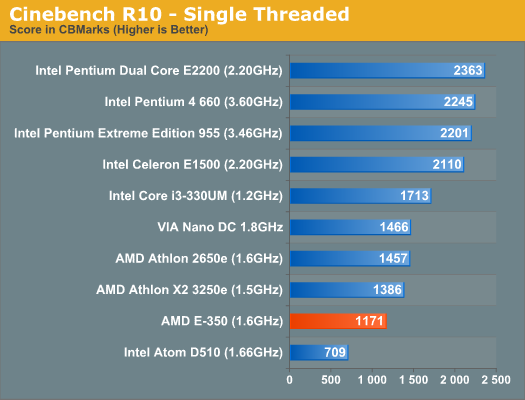
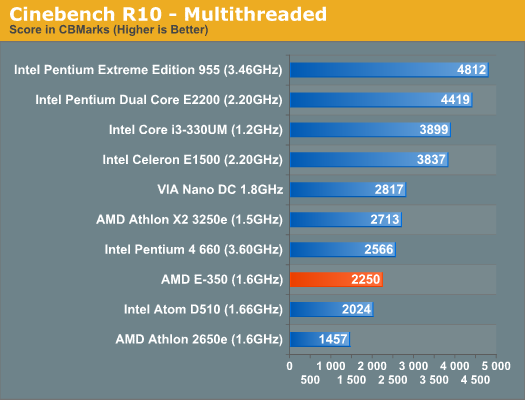
In most of our benchmarks the performance advantage over Atom isn't huge, yet using Brazos is much better than using an Atom based machine. It all boils down to one thing: single threaded performance. Atom can make up for its deficiencies by executing a lot of threads in parallel, but when you're bound by the performance of a single thread the E-350 shines. The E-350 is 65% faster than the Atom D510 in the single threaded Cinebench R10 test. It's this performance advantage that makes the E-350 feel so much quicker than Atom. The Core i3-330UM manages a 46% performance advantage over the E-350. Even in the ultraportable Arrandale ULV space at lower clocks, AMD still leaves a lot of CPU performance on the table. The advantage here will be cost. A single E-350 is less than 40% of the die area of a Core i3-330UM. You may not get the same CPU performance, but performance per mm^2 is much higher.
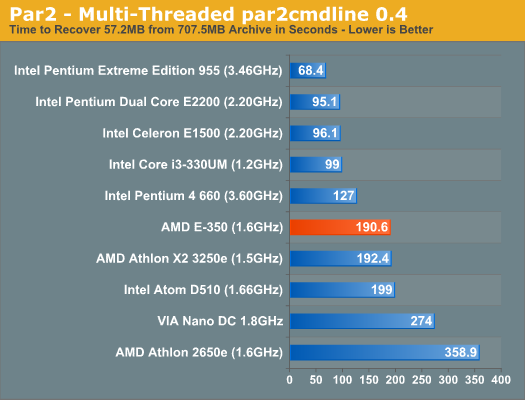
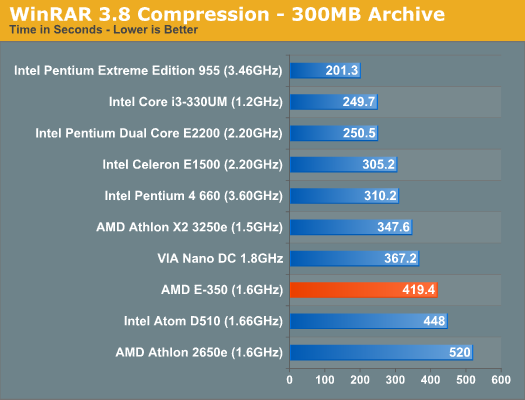
In the multithreaded Cinebench test Atom is able to catch up quite a bit, but the E-350 still holds an 11% advantage. File Compression/Archive Recovery PerformanceOur final two CPU tests are both multithreaded and they show the E-350 equaling and falling behind the performance of the 1.5GHz Athlon X2. As we explained earlier, the gap between the E-350 and Atom shrinks as you add more threads to the workload.
|
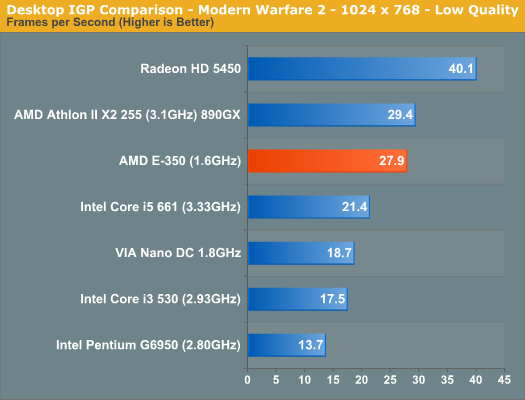
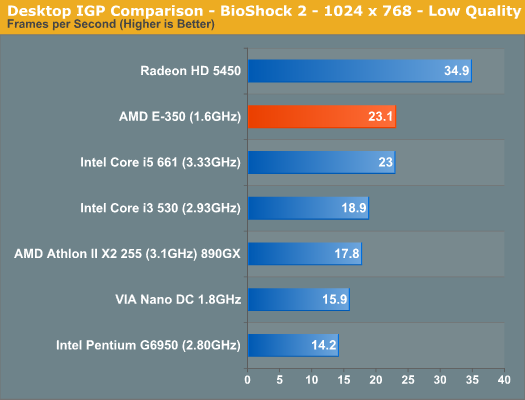
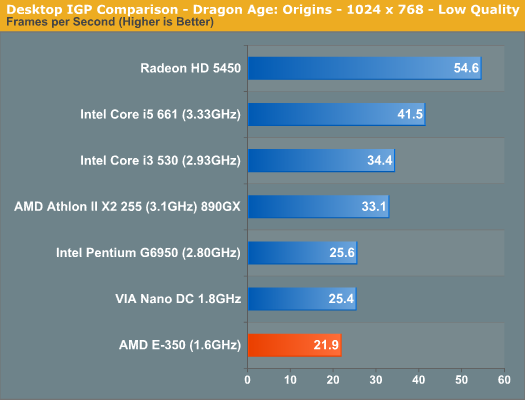
Desktop IGP Comparison: Faster than ClarkdaleI split the graphics comparison into two sections: desktop and mobile. For the desktop section I compared the E-350 to the latest Clarkdale chips, AMD's own 890GX and a discrete Radeon HD 5450 graphics card. While the Radeon HD 5450 has the same number of shader processors as the E-350 (80), they run faster and it has a dedicated 1.6GHz memory bus to feed it. The E-350 has to share memory bandwidth between the two Bobcat cores and the 80 SPs, severely limiting its performance potential.
The E-350 does extremely well compared to its desktop brethren. In our Modern Warfare 2 and BioShock tests its easily faster than the Core i3/i5 and in the case of BioShock 2 it's even faster than AMD's 890GX. Dragon Age Origins is another story however as the benchmark is primarily CPU limited, giving the desktop parts a huge advantage. In GPU bound scenarios, it's clear that our initial Zacate benchmarking was accurate: the E-350's Radeon HD 6310 is quicker than Intel's HD Graphics. Compared to the Radeon HD 5450 the 6310 offers between 66 - 69% of its performance in our GPU bound tests. The performance reduction is entirely due to the 6310's limited memory bandwidth being shared with the dual Bobcat cores on-die.
|
|
Home†††††† Previous††††††† AMD page†††††††† Intel page†††††††† Next |
|
AMD Brazos Lineup |
||||||||
|
APU Model |
Number of Bobcat Cores |
CPU Clock Speed |
GPU |
Number of GPU Cores |
GPU Clock Speed |
TDP |
|
|
|
AMD E-350 |
2 |
1.6GHz |
Radeon HD 6310 |
80 |
500MHz |
18W |
|
|
|
AMD E-240 |
1 |
1.5GHz |
Radeon HD 6310 |
80 |
500MHz |
18W |
|
|
|
AMD C-50 |
2 |
1.0GHz |
Radeon HD 6250 |
80 |
280MHz |
9W |
|
|
|
AMD C-30 |
1 |
1.2GHz |
Radeon HD 6250 |
80 |
280MHz |
9W |
|
|